Dmg Chemical Formula
- Dmg Chemical Formula Calculator
- Dmg Chemical Formula Chart
- Dmg Chemical Formula 2
- Dimethylglyoxime
- Dmg Chemical Formula
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.147 |
| EC Number | |
PubChemCID | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6NiO4 | |
| Molar mass | 176.781 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Green Solid |
| Odor | slight acetic acid |
| Density | 1.798 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.744 g/cm3 (tetrahydrate) |
| Melting point | decomposes when heated [1][2] |
| Easily soluble in cold water, hot water | |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol insoluble in diethyl ether, n-octanol |
| +4,690.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c | |
α = 90°, β = 93.6°, γ = 90°[3] | |
Lattice volume (V) | 471.5 |
| 2 | |
| distorted octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| 350 mg/kg (rat, oral) 410 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[4] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| verify (what is ?) | |
| Infobox references | |
Material Safety Data Sheet Dimethylglyoxime, 1% Alcoholic - 2 - Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. Symptoms may include headache, excitement, fatigue. Enter a chemical formula to calculate its molar mass and elemental composition: Molar mass of Ni(dmg)2 is 288.9146 g/mol Formula in Hill system is C8H14N4NiO4.
Nickel(II) acetate is the name for the coordination compounds with the formula Ni(CH3CO2)2·x H2O where x can be 0, 2, and 4. The green tetrahydrate Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O is most common. It is used for electroplating.
 There are two different types of OS one is Mac OS X Lion 10.7 ISO, DMG and the other one is OS X mountain lion. This for mac is one of the best and successors of 2011 and it is followed by the for mac of 2007.Mac os x lion was released in the month of June on the date of 22nd and in the year of 2011 in the Apple worldwide developers conference. So please don’t get confused in both OS.Mac OS X Lion 10.7 is the eighth major release of Mac OS X is a completely different version from the for windows because it is a version that is totally based on the productivity suite for mac os x.
There are two different types of OS one is Mac OS X Lion 10.7 ISO, DMG and the other one is OS X mountain lion. This for mac is one of the best and successors of 2011 and it is followed by the for mac of 2007.Mac os x lion was released in the month of June on the date of 22nd and in the year of 2011 in the Apple worldwide developers conference. So please don’t get confused in both OS.Mac OS X Lion 10.7 is the eighth major release of Mac OS X is a completely different version from the for windows because it is a version that is totally based on the productivity suite for mac os x.
Synthesis and structure[edit]
The compound can be prepared by treating nickel or nickel(II) carbonate with acetic acid:
- NiCO3 + 2 CH3CO2H + 3 H2O → Ni(CH3CO2)2·4 H2O + CO2
The green tetrahydrate has been shown by X-ray crystallography to adopt an octahedral structure, the central nickel centre being coordinated by four water molecules and two acetate ligands.[5] It may be dehydrated in vacuo, by reaction with acetic anhydride,[6] or by heat.[7]
Dmg Chemical Formula Calculator
Safety[edit]
Nickel salts are carcinogenic and irritate the skin.
References[edit]
- ^M. A. Mohamed, S. A. Halawy, M. M. Ebrahim: 'Non-isothermal decomposition of nickel acetate tetrahydrate', in: Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1993, 27 (2), S. 109–110. doi:10.1016/0165-2370(93)80002-H.
- ^G. A. M. Hussein, A. K. H. Nohman, K. M. A. Attyia: 'Characterization of the decomposition course of nickel acetate tetrahydrate in air', in: Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 1994, 42, S. 1155–1165; doi:10.1007/BF02546925.
- ^Downie, T. C.; Harrison, W.; Raper, E. S.; Hepworth, M. A. (15 March 1971). 'A three-dimensional study of the crystal structure of nickel acetate tetrahydrate'. Acta Crystallographica Section B. 27 (3): 706–712. doi:10.1107/S0567740871002802.
- ^'Nickel metal and other compounds (as Ni)'. Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^Van Niekerk, J. N.; Schoening, F. R. L. (1953). 'The crystal structures of nickel acetate, Ni(CH3COO)2·4H2O, and cobalt acetate, Co(CH3COO)2·4H2O'. Acta Crystallogr.6 (7): 609–612. doi:10.1107/S0365110X5300171X.
- ^Lascelles, Keith; Morgan, Lindsay G.; Nicholls, David; Beyersmann, Detmar (2005). 'Nickel Compounds'. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_235.pub2.
- ^Tappmeyer, W. P.; Davidson, Arthur W. (1963). 'Cobalt and Nickel Acetates in Anhydrous Acetic Acid'. Inorg. Chem.2 (4): 823–825. doi:10.1021/ic50008a039.
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 BeAcOH | B(OAc)3 | AcOAc ROAc | NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaOAc | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al2SO4(OAc)4 | Si | P | S | ClAc | Ar | ||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 | Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 | Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 | Co(OAc)2, Co(OAc)3 | Ni(OAc)2 | Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc | Kr |
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru(OAc)2 Ru(OAc)3 Ru(OAc)4 | Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 | Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc | Xe |
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au | Hg2(OAc)2, Hg(OAc)2 | TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 | Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 | Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)x | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er | Tm | Yb(OAc)3 | Lu(OAc)3 | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | |
| Other names Nickel hydroxide, Theophrastite | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.813 |
| EC Number |
|
| RTECS number | |
CompTox Dashboard(EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ni(OH)2 | |
| Molar mass | 92.724 g/mol (anhydrous) 110.72 g/mol (monohydrate) |
| Appearance | green crystals |
| Density | 4.10 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 230 °C (446 °F; 503 K) (anhydrous, decomposes) |
| 0.13 g/L | |
| +4500.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure[1] | |
| hexagonal, hP3 | |
| P3m1, No. 164 | |
α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 120° | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 79 J·mol−1·K−1[2] | |
Std enthalpy of formation(ΔfH⦵298) | −538 kJ·mol−1[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External SDS |
| GHS pictograms | [3] |
| GHS Signal word | Danger[3] |
| H302, H332, H315, H334, H317, H341, H350, H360, H372[3] | |
| P260, P284, P201, P280, P405, P501[3] | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| 1515 mg/kg (oral, rat) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| verify (what is ?) | |
| Infobox references | |
Nickel(II) hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ni(OH)2. It is an apple-green solid that dissolves with decomposition in ammonia and amines and is attacked by acids. It is electroactive, being converted to the Ni(III) oxy-hydroxide, leading to widespread applications in rechargeable batteries.[4]
Properties[edit]
Nickel(II) hydroxide has two well-characterized polymorphs, α and β. The α structure consists of Ni(OH)2 layers with intercalated anions or water.[5][6] The β form adopts a hexagonal close-packed structure of Ni2+ and OH− ions.[5][6] In the presence of water, the α polymorph typically recrystallizes to the β form.[5][7] In addition to the α and β polymorphs, several γ nickel hydroxides have been described, distinguished by crystal structures with much larger inter-sheet distances.[5]
The mineral form of Ni(OH)2, theophrastite, was first identified in the Vermion region of northern Greece, in 1980. It is found naturally as a translucent emerald-green crystal formed in thin sheets near the boundaries of idocrase or chlorite crystals.[8] A nickel-magnesium variant of the mineral, (Ni,Mg)(OH)2 had been previously discovered at Hagdale on the island of Unst in Scotland.[9]
Dmg Chemical Formula Chart
Reactions[edit]
Nickel(II) hydroxide is frequently used in electrical car batteries.[6] Specifically, Ni(OH)2 readily oxidizes to nickel oxyhydroxide, NiOOH, in combination with a reduction reaction, often of a metal hydride (reaction 1 and 2).[10]
Dmg Chemical Formula 2
Reaction 1 Ni(OH)2 + OH− → NiO(OH) + H2O + e−
Reaction 2 M + H2O + e− → MH + OH−
Net Reaction (in H2O)Ni(OH)2 + M → NiOOH + MH
Of the two polymorphs, α-Ni(OH)2 has a higher theoretical capacity and thus is generally considered to be preferable in electrochemical applications. However, it transforms to β-Ni(OH)2 in alkaline solutions, leading to many investigations into the possibility of stabilized α-Ni(OH)2 electrodes for industrial applications.[7]
Synthesis[edit]
The synthesis entails treating aqueous solutions of nickel(II) salts with potassium hydroxide.[11]
Toxicity[edit]
The Ni2+ ion is a known carcinogen. Toxicity and related safety concerns have driven research into increasing the energy density of Ni(OH)2 electrodes, such as the addition of calcium or cobalt hydroxides.[4]
See also[edit]
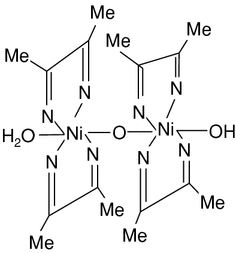
Dimethylglyoxime
References[edit]
- ^Enoki, Toshiaki; Tsujikawa, Ikuji (1975). 'Magnetic Behaviours of a Random Magnet, NipMg(1-p)(OH2)'. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan. 39 (2): 317. doi:10.1143/JPSJ.39.317.
- ^ abZumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A22. ISBN978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ abcd'Nickel Hydroxide'. American Elements. Retrieved 2018-08-30.
- ^ abChen, J.; Bradhurst, D.H.; Dou, S.X.; Liu, H.K. (1999). 'Nickel Hydroxide as an Active Material for the Positive Electrode in Rechargeable Alkaline Batteries'. J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 (10): 3606–3612. doi:10.1149/1.1392522.
- ^ abcdOliva, P.; Leonardi, J.; Laurent, J.F. (1982). 'Review of the structure and the electrochemistry of nickel hydroxides and oxy-hydroxides'. Journal of Power Sources. 8 (2): 229–255. doi:10.1016/0378-7753(82)80057-8.
- ^ abcJeevanandam, P.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. (2001). 'Synthesis of Nanosized α-Nickel Hydroxide by a Sonochemical Method'. Nano Letters. 1 (5): 263–266. doi:10.1021/nl010003p.
- ^ abShukla, A.K.; Kumar, V.G.; Munichandriah, N. (1994). 'Stabilized α-Ni(OH)2 as Electrode Material for Alkaline Secondary Cells'. J. Electrochem. Soc. 141 (11): 2956–2959. doi:10.1149/1.2059264.
- ^Marcopoulos, T.; Economou, M. (1980). 'Theophrastite, Ni(OH)2, a new mineral from northern Greece'(PDF). American Mineralogist. 66: 1020–1021.
- ^Livingston, A.; Bish, D. L. (1982). 'On the new mineral theophrastite, a nickel hydroxide, from Unst, Shetland, Scotland'(PDF). Mineralogical Magazine. 46 (338): 1. doi:10.1180/minmag.1982.046.338.01.
- ^Ovshinsky, S.R.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Ross, J. (1993). 'A nickel metal hydride battery for electric vehicles'. Science. 260 (5105): 176–181. doi:10.1126/science.260.5105.176. PMID17807176.
- ^Glemser, O. (1963) 'Nickel(II) Hydroxide' in 'Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd ed. G. Brauer (ed.), Academic Press, NY. Vol. 1. p. 1549.